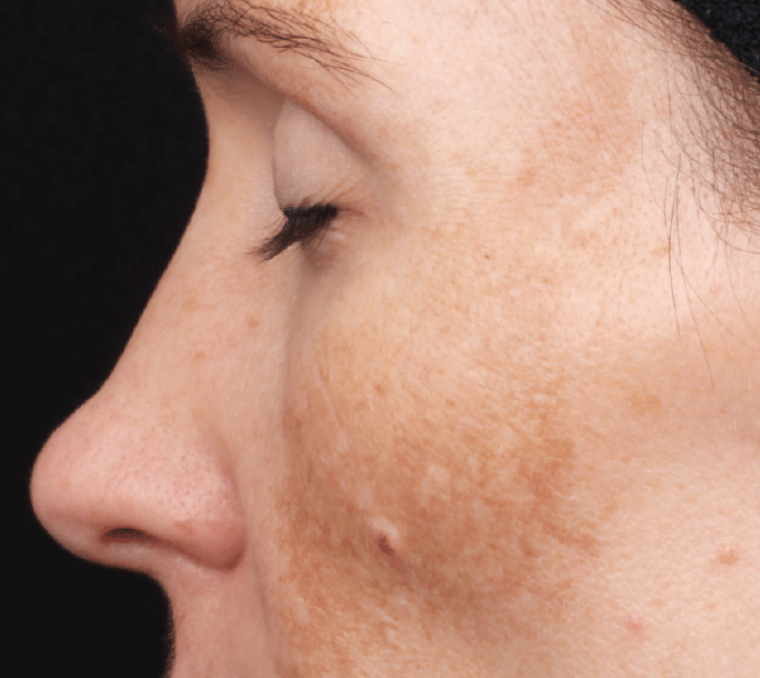
Hyperpigmentation, also known as Melasma, is a condition that occurs when areas of skin produce an excess of melanin (the substance that gives skin its colour), causing these areas to become darker than the surrounding skin. Hyperpigmentation affects all ages, races and skin types. Age spots, sun spots, dark patches or skin discolouration – whatever you call it, all of these are examples of hyperpigmentation.
The Causes:
Sun Damage
The sun’s UV rays are melanin’s main reason for existing. This pigment acts as a natural sunscreen to prevent skin damage from the sun’s harsh rays. Any concentrated patches of excess melanin on the face, neck, chest, hands and other areas exposed to the sun will inevitably become darker, just as tanning leads to increased production of pigment in the skin cells, and therefore, darker skin.
Injury or Inflammation
Those with sensitive skin that easily develop hyperpigmentation will know that dark spots can develop after any inflammation or injury to the skin, from cuts and burns to rashes or even common acne and bug bites. Extra melanin can be produced during the process whereby the skin repairs itself, and so it is essential not to pick at spots or scabs as they heal in order to avoid these side effects.
Stress and Hormonal Changes
One of the most challenging but easiest culprits to manage is stress. When stress increases, cortisol in the body increases, which in turn affects the balance of a woman’s hormones – estrogen and progesterone. Research also shows that more often than not, pregnant women or women who are taking certain oral contraceptives are more prone to hyperpigmentation. This could come down to medication side effects and/or natural hormonal changes.
How to Treat Hyperpigmentation
First things first – treat the causes! When you do spend time outdoors, stay out of the sun as much as possible and use a high SPF of 40 to 50 sunscreen, applied every 2 hours. Take good care of your skin and avoid picking scabs and spots to ensure they heal quickly without accumulating pigment around the site of a skin inflammation or injury.
Now to treat existing hyperpigmentation.
Treatment requires a multi-functional approach to target all aspects of the melanin formation process. Ingredients such as pigment inhibitors, antioxidants such as Niacinamide, Vitamin C, Retinol and a blend of Alpha Hydroxy Acids in the right concentration and strength assist in alleviating hyperpigmentation.
Several skin treatments and ingredients have shown promise in relieving dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
Glycolic Acid:
This is a plant-based ingredient that speeds up cell turnover, allowing hyperpigmented skin cells to be shed to reveal the new, undamaged skin beneath. Glycolic acid is commonly used in skincare clinics and by dermatologists as part of a chemical peel that is designed to leave the skin more even in both colour and texture.
Lactic Acid:
Another common foundation for chemical peels, lactic acid is considered a milder option than glycolic acid, and so is well matched to sensitive skin. In addition to evening out skin tone, lactic acid is also believed to minimise pore size and improve texture.
The Bottom Line
If dark spots are affecting your confidence, it’s great to know there are several things you can do to address them head-on! Always speak to a skincare specialist or dermatologist before exploring new products or unfamiliar treatments, and there’s a good chance you’ll be able to turn back the years to a more youthful you.
As we’ve seen above, though, avoiding developing dark spots in the first place is all about lifestyle, so make sure you treat your skin with respect and protect it from that harsh South African sun when you go outdoors.